جارى التحميل
استخدم زر ESC أو رجوع للعودة
Allergy testing involves having a skin or blood test to find out what substance, orallergen, may trigger an allergic response in a person. Skin tests are usually done because they are rapid, reliable, and generally less expensive than blood tests, but either type of test may be used.
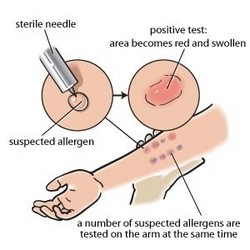
Skin tests
Skin prick test~
This test is done by placing a drop of a solution containing a possible allergen on the skin, and a series of scratches or needle pricks allows the solution to enter the skin.
If the skin develops a red, raised itchy area (called a wheal), it usually means that the person is allergic to that allergen. This is called a positive reaction.
Intradermal test~
During this test, a small amount of the allergen solution is injected into the skin.
An intradermal allergy test may be done when a substance does not cause a reaction in the skin prick test but is still suspected as an allergen for that person.
The intradermal test is more sensitive than the skin prick test but is more often positive in people who do not have symptoms to that allergen (false-positive test results).
Skin patch test~
For a skin patch test, the allergen solution is placed on a pad that is taped to the skin for 24 to 72 hours. This test is used to detect a skin allergy called contact dermatit
Blood tests
In those situations where skin tests cannot be done, a doctor may use blood tests such as ELISA.
These tests measure the presence of food-specific IgE antibodies in the blood of patients, but they cost more than skin tests, and the results are not available immediately.
As with positive skin tests, positive blood tests make the diagnosis of a specific food allergy only when the clinical history is compatible.
Food challenge: The double-blind food challenge has become the gold standard for objective allergy testing.
In this test, various foods, some of which are suspected of inducing an allergic reaction, are placed in individual opaque capsules
. Both the patient and the doctor are blinded, so that neither of them knows which capsules contain the suspected allergens.
(The capsules are prepared by another medical worker.) The patient swallows a capsule and the doctor then observes whether an allergic reaction occurs.
This process is repeated with each capsule. Alternatively, the food to be tested may be disguised in another type of food to which the person is not allergic.
The advantage of a food challenge is that if the patient has an allergic reaction only to the suspected foods and not to the other foods tested, the diagnosis of food allergy is confirmed.
حينما تعمل العمل فلا تعجب به فقد لا تنال من اجره شيئاً
ولا تحتقر صغير العمل فقد ترفع به
http://kenanaonline.com/medicalanalysis




ساحة النقاش