Tachypleus gigas is one of the four extant species of horseshoe crab. It is found in shallow water in South East Asia at depths of up to 40 m (130 ft). It grows up to 39 cm (15 in) long and 17.5 cm (6.9 in) wide, and is covered by a sturdy carapace, with a long caudal spine (tail).
Description
Tachypleus gigas has a "sage green" chitinous exoskeleton. In a sample of five individuals, Lazarus et al. recorded maximum and minimum total lengths of 39 centimetres (15 in) and 27 cm (11 in), respectively. The prosoma is the widest part of the animal, at 14–17.5 cm (5.5–6.9 in) and 8.2–11.5 cm (3.2–4.5 in) long, while the opisthosoma is 9–11.5 cm (3.5–4.5 in) wide and 6–7.5 cm (2.4–3.0 in) long. The caudal spine (the long, pointed part of the tail) is 13.5–19 cm (5.3–7.5 in) long, bears a crest dorsally, and is concave ventrally. The anterior part of the tail is sharply serrated. Males are smaller than females, have a paler and rougher carapace, and act as hosts to a greater number of epibionts.
The carapace which shields the prosoma also bears two pairs of eyes – a pair of simple eyes at the front, and a pair of compound eyes positioned laterally. In common with other horseshoe crabs, T. gigas also has ventral eyes near the mouthparts, and photoreceptors in the caudal spine.
On the underside of the animal, T. gigas has seven pairs of legs, five of which bear small claws, and five pairs of book gills, which are used for gas exchange.


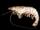
ساحة النقاش