الاطار النظري للمحاسبة Conceptual Framework
1- A conceptual framework is like constitution that leads the accounting system.
الاطار النظري للمحاسبة يشبه الدستور الذي يقود النظام المحاسبي
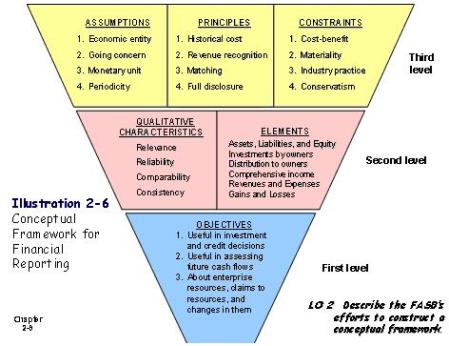
2- The conceptual framework is made of three levels:
Level (1) Objectives of financial reporting
Level (2): (A) Qualitative characteristics of accounting information and (B) Elements of financial statements.
Level (3): Recognition and measurement concepts: (Assumptions, Principles, and Constraints).
الاطار النظري للمحاسبة مكون من ثلاث مستويات:
المستوى الاول: اهداف الابلاغ المالي
المستوى الثاني: (أ) الخصائص النوعية للمعلومات المحاسبية، و(ب) عناصر القوائم المالية
المستوى الثالث: مفاهيم القياس والاعتراف (الفروض والمباديء والمحددات).
Level (1) Objectives of financial statements
المستوى الاول: اهداف القوائم المالية
Objectives of financial reporting are to provide information that is: (1) useful to those making investment and credit decisions, (2) helpful to present and potential investors, creditors, and other users in assessing the amounts, timing, and uncertainty of future cash flows, and (3) about economic resources, the claims to those resources and the changes in them.
اهداف الابلاغ المالي هو نزويد معلومات: (1) مفيده لمتخي القرارات الاستثمارية والائئتمانية، (2) مساعده للمستثمرين والدائنين تمكنهم من تقدير المبالغ، والتوقيت، وعدم الاكيدية من التدفقات النقدية المستقبلية، و (3) والخاصة بالموارد الاقتصادية، والمطالبات الخاصة بتلك الموارد واي تغييرات تطرأ عليها.
Level (2) (A) Qualitative characteristics of accounting information
المستوى الثاني: (أ) الخصائص النوعية للمعلومات المحاسبية
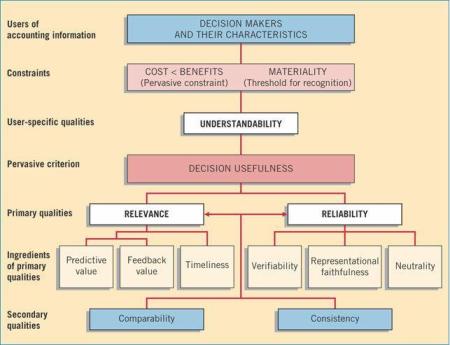
1- Decision makers and their characteristics (Understandability)
متخذو القرار وخصائصهم (القابلية للفهم)
2- Constraints: (1) Cost < Benefits, and (2) Materiality
المحددات الرئيسية: (1) ان تكون التكلفة اقل من المنفعة و(2) الاهمية النسبية
3- Primary qualities: (1) Relevance, and (2) Reliability
الخصائص الرئيسية: (1) الملاءمة و(2) الموثوقية
4- Ingredients of primary qualities: (1) Relevance (a- predictive value, b- feedback value, and c- timeliness), and (2) Reliability (a- verifiability, b- representational faithfulness, and c- neutrality)
مكونات الخصائص الرئيسية: (1) الملاءمة (أ- القيمة التنبئية، ب- القيمة الاسترجاعية وج- التوقيت المناسب)، و(2) الموثوقية (أ- القدرة على التحقق، ب- الصدق في العرض، وج- الحيادية
5- Secondary qualities: (1) comparability, and (2) consistency
الخصائص الثانوية (1) القدرة على المقارنة و (2) الثبات.
Level (2) (B) Elements of financial statements
المستوى الثاني (ب) عناصر القوائم المالية
1- Assets: probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a particular entity as a result of past transactions or events
الاصول: منافع اقتصادية مستقبلية محتملة تم التحصل عليها او السيطرة عليها من قبل منشأه ناتجة عن احداث او عمليات سابقة
2- Liabilities: probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of a particular entity to transfer assets or providing services to other entities as a result of past transactions or events
الالتزامات: تضحيات مستقبلية محتملة لمنافع اقصادية تنشأ عن تعهدات حالية من قبل منشأه لمنشأه اخرى مقابل تحويل اصول او تقديم خدمات ناتجة عن احداث او عمليات سابقة
3- Equity: residual interest in the assets of an entity that remains after deducting its liabilities. In a business enterprise, the equity is the ownership interest.
حصة السهم: وهي الحصة في اصول المنشأة بعد اقتتاع الالتنزامات منها. وهذه الحصة يطلق عليها في الشركات التجارية بحصة حقوق الملكية
4- Revenues: inflows or other enhancements of assets of an entity or settlement of liabilities (or a combination of both) during a period from delivering or producing goods, rendering services, or activities that constitute the entity ongoing major or control operations.
الايرادات: وهي تدفقات واردة أو مساهمات اصول المنشأة او تسوية التزاماتها (او كلاهما) خلال فترة تسليم او تصنيع البضائع، تأدية الخدمات، او الفاعاليات التي تساهم في استمرارية او السيطرة على نشاط المنشأة الرئيسي
5- Expenses: outflows or other using up of assets or incurrence of liabilities (or a combination of both) during a period from delivering or producing goods, rendering services, or carrying out other activities that constitute the entity ongoing major or control operations.
المصروفات: وهي تدفقات صادرة او استخدمات اخرى للاصول او التعهد بالتزامات (او كلاهما) خلال فترة تسليم او تصنيع البضائع، تأدية الخدمات، او الفاعاليات التي تساهم في استمرارية او السيطرة على نشاط المنشأة الرئيسي
6- Gains: increases in equity (net assets) from peripheral or incidental transactions of an entity during a period except those that result from revenues or investments by owners.
المكاسب: زيادة في حقوق الملكية (صافي الاصول) ناتجه عن عمليات للمنشأة عرضية او خارجية خلال فترة محدده مستثنى منها تلك الناتجة عن الايرادات و استثمارات الملاك.
7- Losses: decreases in equity (net assets) from peripheral or incidental transactions of an entity and from all other transactions and other events and circumstances affecting the entity during a period except those that result from expenses or distribution to owners.
الخسائر: نقص في حقوق الملكية (صافي الاصول) ناتجه عن عمليات للمنشأة عرضية او خارجية وناتجة كذلك من جميع العمليات والاحداث والظروق المؤثرة على المنشأة خلال فترة محدده مستثنى منها تلك الناتجة عن المصاريف وتوزيعات الملاك
Level (3) Recognition and Measurement Concepts
المستوى الثالث مفاهيم القياس والاعتراف
A- Basic Assumptions (الفروض الاساسية)
1- Economic Entity Assumption means that economic activity can be identified with a particular unit of accountability.
فرض الوحدة الاقتصادية تعني بانه يمكن تعريف نشاطات الوحده الاقتصادية من خلال وحده قياس محاسبية محدده
2- Going Concern Assumption means that the business enterprise will have long life.
فرض الاستمراية يعني بان عمر المنشأة طويل وغير محدد
3- Monetary Unit Assumption means that money is the common denominator of economic activity and provides an appropriate basis for accounting measurement and analysis.
فرض الوحدة النقدية يعني بأن المال هو وحدة القياس الرئيسية للنشاطات الاقتصادية وهو الاساس في القياس والتحليل المحاسبي
4- Periodicity Assumption means that the economic activities of an enterprise can be divided into artificial time periods.
فرض الدورية يعني يمكن تقسيم نشاطات المنشأة الاقتصادية الى فترات زمنية اعتبارية
B- Basic Principles of Accounting (مبادئ المحاسبة الاساسية)
1- Historical Cost Principle means that most assets and liabilities to be accounted for and reported on the basis of acquisition price.
مبدأ التكلفة التاريخية يعني بانه يجب احتساب قيمة الاصول والالتزامات والابلاغ عنها وفقا لسعر التملك (بتاريخ العملية)
2- Revenue Recognition Principle means that revenue should be recognized when (1) realized or realizable and (2) when earned.
مبدأ الاعتراف بالايراد يعني بانه يجب الاعتراف بالايراد عندما (1) يتحقق او يكون قابل للتحقق و(2) عند اكتسابه
- Revenues are Realized when products (goods or services), merchandise, or other assets are exchanged for cash or claims to cash.
يتحقق الايراد عندما يتم تبادل المنتجات (البضائع او الخدمات) و البضائع او الاصول الاخرى بالنقد او الطالبات النقدية
- Revenues are realizable when assets received or held are ready convertible into cash or claims to cash.
يكون الايراد قابلا للتحقق اذا كانت الاصول المستلمة او التي بالحوزة قابله للتحويل الى نقد او مطالبات نقدية
- Revenues are considered earned when the entity has substantially accomplished what it must do to be entitled to the benefits represented by the revenues.
يتم اعتبار الايراد مكتسبا اذا اعتبرته المنشأة ايرادا منجز بشكل كامل وتم التحصل عليه واستخدامه لمنفعتها
Ways of revenue recognition طرق الاعتراف بالايراد (التوقيت)
- Recognition at the time of sale provides a uniform and reasonable test.
توقيت الاعتراف عند نقطة البيع هو انسب توقيت بشكل عام
- During production: Recognition of revenue is allowed before the contract is completed in certain long-term construction contracts.
خلال عملية الانتاج: يتم السماح بالاعتراف بالايراد خلال عملية الانتاج في تعهدات البناء طويلة الاجل
- End of production: revenue might be recognized after the production has ended but before the sale takes place.
بعد الانتهاء من الانتاج: يمكن الاعتراف بالايراد بعد عملية الانتاج ولكن قبل ان تتم عملية البيع
- Receipt of cash: its used only when its impossible to establish the revenue figure at the time of sale because of the uncertainty of collection.
عند ستلام النتقد: يتم الاعتراف بالايراد عند استلام النقد عندما لا يمكن تحديد عنصر الايراد عند عملية البيع لعدم اكطيدية تحصيل النقد كالبيع بالتقسيط
3- Matching Principle dictates that efforts (expenses) be matched with accomplishment (revenues) whenever it is reasonable and practicable to do so.
ان مبدأ المقابلة ينص على مقابلة المجهودات (المصاريف) بالانجازات (الايرادات) كلما دعت الحاجة لذلك
4- Full disclosure Principle recognizes that the nature and amount of information included in financial reports reflects a series of judgmental trade-offs. These trade-offs strive for (1) sufficient detail to disclose maters that makes a difference to users, yet (2) sufficient condensation to make the information understandable, keeping in mind costs of preparing and using it. Information about financial position, income, cash flows, and investments can be found in one of the following three places: (1) financial statements, (2) notes to the financial statements, and (3) supplementary information.
مبدأ الافصاح الشامل يعرف حجم وطبيعة المعلومات المشمولة في الابلاغ المالي والتي تعكس الحكم الجاد في مقارنة الامور. حيث ينص على تزويد (1) الافصاح الكافي عن الامور التي تحدث فرقا للمستخدمين المختلفين للقوائم، ومع الاخذ بعين الاعتبار (2) بجعل المعلومات قابلة للفهم وتكلفة اعدادها واستخدامها. يمكن ايجاد المعلومات الخاصة بالمركز المالي والدخل والتدفقات النقدية والاستثمارات في احد الاماكن التالية: (1) القوائم المالية، و(2) ملاحظات القوائم المالية و(3) وقوائم المعلومات التكميلية او الاضافية
Constraints (المحددات-قيود)
1- Cost-Benefit Relationship means that the cost of providing the information must be weighted against the benefits that can be derived from using the information.
علاقة التكلفة والمنفعة تعني بانه يجب موازنة تكلفة تزويد المعلومات بالمنفعة المترتبة على استخدامها
2- Materiality relates to an items impact on a firms overall financial operations. An item is material if its inclusion or omission would influence or change the judgment of a reasonable person. It is immaterial and, therefore, irrelevant if it would have no impact on decision-maker.
ان الاهمية النسبية تعود الى مدى تاثير بند معين على العمليات المالية ككل. يعد البند مهم اذا كان تضمينه او حذفه سيؤثر او يغير حكم شخص عقلاني. ويعد غير مهم اذا كان تضمينه او حذفه ليس له اثر على متخذ القرار.
3- Industry Practices means the peculiar nature of some industries and business concerns sometimes requires departure from basic theory.
محددات الصناعة تعني بان طبيعة بعض الصناعات والتجارة تجعلها تحيد عن النظرية العامة.
4- Conservatism means when in doubt choose the solution that will be least likely to overstate assets and income.
التحفظ (الحيطة والحذر) يعني بانه عند تولد اي شك فانه يجب اختيار ذلك الحل الذي لا يغالي في تقدير الاصول والدخل